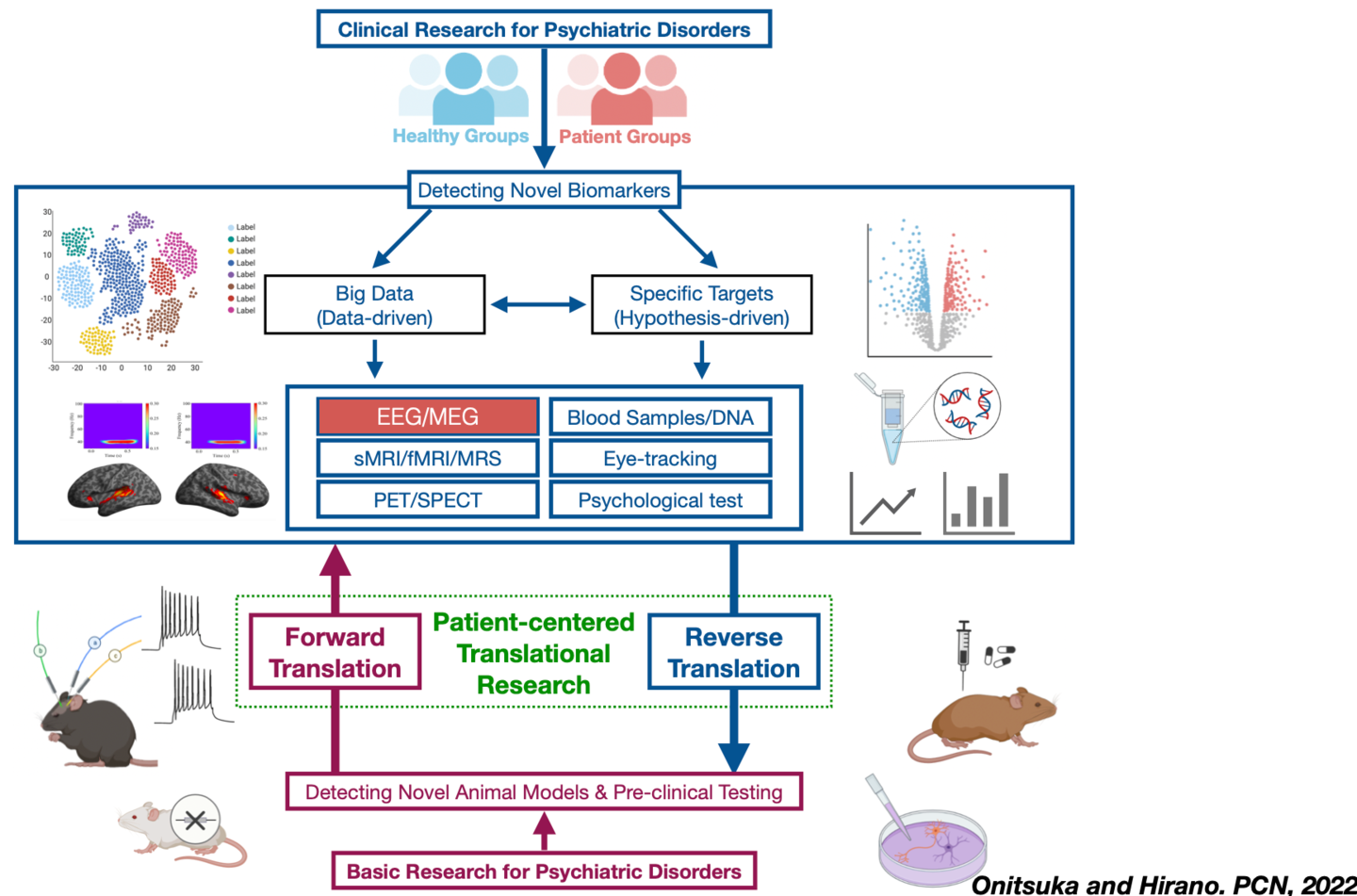
Importance of Electroencephalography (EEG) Studies in Bidirectional Translational Research
Clinical research needs to detect novel biomarkers, by focusing on specific targets (hypothesis-driven) or using big data (data-driven), that are translatable to basic research. Basic research needs to detect novel animal models that would be useful for preclinical testing. These clinical and basic studies need to be performed bidirectionally through forward translation and reverse translation to achieve patient-centered translational therapeutic research. Neurophysiological studies using electroencephalography (EEG) play a vital role in bidirectional translational research because EEG data can be obtained in both humans and animals.
Multi-center EEG Biomarker Studies in JAPAN
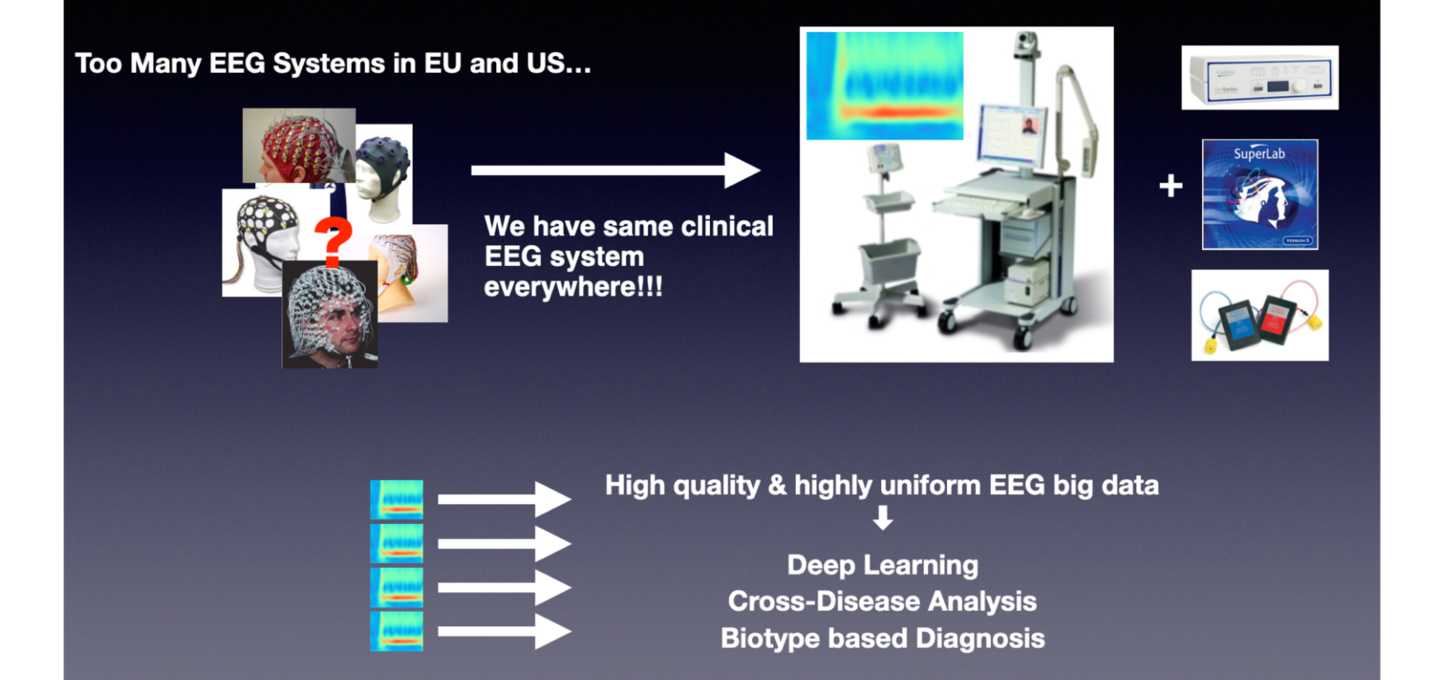
Recently, large-sample collaborative studies are becoming crucial to characterize healthy and clinical population groups in psychiatric research. Importantly, multicenter studies may also greatly benefit from adapting statistical models correcting for the effects of each site. It should be noted that by taking advantage of the fact that only one EEG company (Nihon Kohden) is approved for clinical use in Japan, we can conduct large-sample collaborative EEG studies using the same or very similar EEG systems (with the same stimulus presentation, recording environment, and data collection procedures) in Japan.